The term “warped brake disc” has been in common use in motor racing for decades. When a driver reports a vibration under hard braking, inexperienced crews, after checking for (and not finding) cracks often attribute the vibration to “warped discs”. They then measure the disc thickness in various places, find significant variation and the diagnosis is cast in stone. When disc brakes for high performance cars arrived on the scene we began to hear of “warped brake discs” on road going cars, with the same analyses and diagnoses.
Typically, the discs are resurfaced to cure the problem and, equally typically, after a relatively short time the roughness or vibration comes back. Brake roughness has caused a significant number of cars to be bought back by their manufacturers under the “lemon laws”. 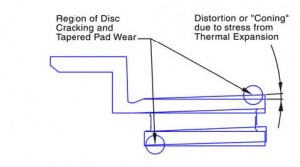
This has been going on for decades now – and, like most things that we have cast in stone, the diagnoses are wrong. With one qualifier, presuming that the hub and wheel flange are flat and in good condition and that the wheel bolts or hat mounting hardware is in good condition, installed correctly and tightened uniformly and in the correct order to the recommended torque specification, in more than 40 years of professional racing, including the Shelby/Ford GT 40s – one of the most intense brake development program in history – I have never seen a warped brake disc.
I have seen lots of cracked discs, discs that had turned into shallow cones at operating temperature because they were mounted rigidly to their attachment bells or top hats, a few where the friction surface had collapsed in the area between straight radial interior vanes, and an untold number of discs with pad material unevenly deposited on the friction surfaces sometimes visible and more often not.
Article written by Carroll Smith, Consulting Engineer at StopTech